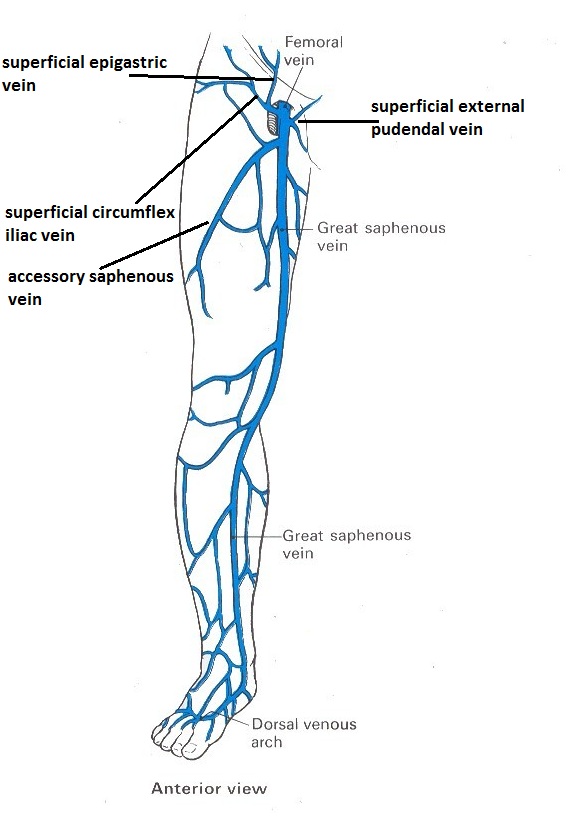
The Great Saphenous Vein
Definition
Is a large subcutaneous vein of the lower limb
It is the longest vein in the body running along the length of the lower limb
Origin
Originates from where the dorsal vein of the great toe joins with the dorsal venous arch of the foot.
Course
It passes in front of the meidal malleolus - it is seen well here and can be palpated.
Runs up the medial side of the leg.
At the knee, it runs over the posterior border of the medial epicondyle of the femur.
Then courses anteriorly and lies on the anterior surface of the thigh.
Enters an opening in the fascia lata called the saphenous opening.
There it joins the common femoral vein in the femoral triangle; it is called saphenofemoral junction.
Tributaries
At the ankle medial marginal vein from sole of foot
At the lower leg - freely anastomoses with small saphenous vein
Communicates by perforator veins with the anterior and posterior tibial veins
Many cutaneous veins
Near the knee communicates with the popliteal vein by the Boyd perforator
in the thigh communicates with the femoral vein by perforator veins (Dodd perforator)
Receives numerous tributaties through accessory saphenous vein near the sapheno-femoral junction
Near the fossa ovalis it receives the tributaries : Superficial epigastric vein, superficial external pudental vein and superficial circumflex iliac vein - Which have to be ligated carefully to prevent recurrence of varicosity during stripping of the great saphenous vein.
Clinical Importance
Varicose veins
Thrombophlebitis
Immobilization → thrombosis → pulmonary thromboembolism
GSV used in cardiac bypass surgery
Saphenous nerve - a branch of the femoral nerve - runs with GSV and can be damaged in surgery on the vein
* * * * * * * * * * * * *